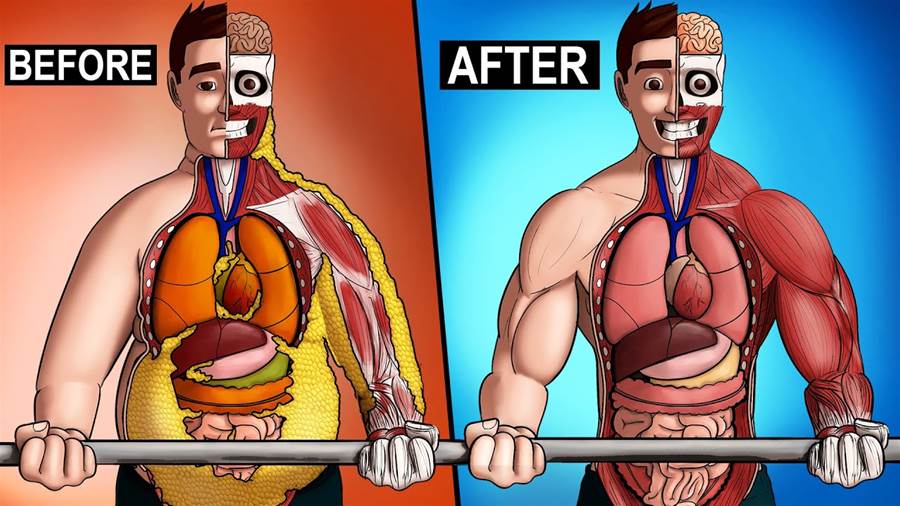

Exercise triggers a multitude of physiological changes in your body, affecting everything from your heart and lungs to your brain and hormones. Here’s a step-by-step look at what happens inside your body when you exercise and how these changes contribute to overall fitness and well-being.

Energy Production and Demand
When you exercise, your muscles require more energy, primarily in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ATP is the energy currency of your cells, and your body only has a limited supply on hand. To meet the increased energy demands, your body rapidly creates more ATP.
One key process for generating ATP is glycolysis. This process converts glucose, a type of sugar derived from the food you eat, into ATP. Glucose is stored in your muscles and liver, ready to be broken down quickly to fuel your workout. However, glycolysis alone isn't enough to meet all energy needs, especially during intense exercise.
As you continue to exercise, your body also increases its demand for oxygen. Oxygen helps generate ATP more efficiently, which is why your heart rate and breathing rate rise during physical activity.
The article is not finished. Click on the next page to continue.














代表者: 土屋千冬
郵便番号:114-0001
住所:東京都北区東十条3丁目16番4号
資本金:2,000,000円
設立日:2023年03月07日
